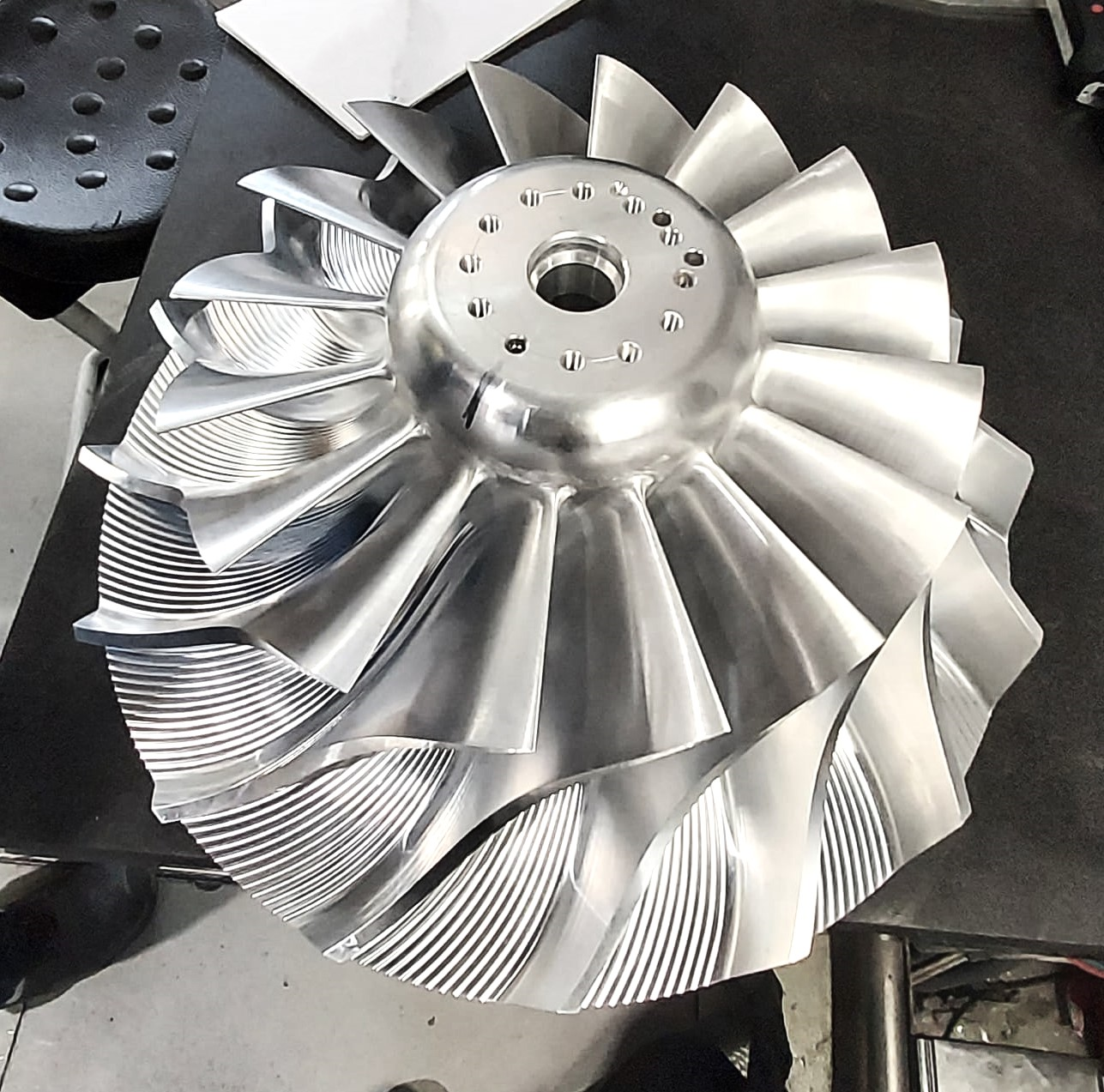
Compressor wheels and expander impellers play crucial roles in the functionality of various mechanical systems, ranging from automotive turbochargers to industrial gas turbines. In this article, we will delve into the essential aspects of inspecting these components, understanding their significance, and ensuring optimal performance.
Compressor wheels and expander impellers are integral components in systems that involve the compression and expansion of gases. Compressor wheels are commonly found in turbochargers, where they compress air before it enters the engine. Expander impellers, on the other hand, are utilized in applications such as power recovery from exhaust gases.
1. How to inspect
1.1. Material and Manufacturing Quality:
Begin the inspection by assessing the material and manufacturing quality of the compressor wheel and expander impeller. Look for any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. High-quality materials, such as aerospace-grade aluminum or stainless steel, contribute to the durability and efficiency of these components.
1.2. Blade Condition:
Examine the blades of the compressor wheel and expander impeller for any signs of erosion, pitting, or distortion. These issues can negatively impact the efficiency of the compression or expansion process. Ensure that the blades are intact, properly aligned, and free from any foreign objects that may have entered the system.
1.3. Balancing and Vibration Analysis:
Proper balancing is critical for the smooth operation of compressor wheels and expander impellers. Check for any imbalance that may lead to increased vibration. Excessive vibration can result in premature wear and potential failure. Employ vibration analysis tools to identify and address any imbalance issues.
1.4. Clearances and Tolerances:
Pay attention to the clearances and tolerances within the compressor wheel and expander impeller assembly. Improper clearances can lead to reduced efficiency and increased friction. Measure and compare the clearances against manufacturer specifications, making adjustments as necessary.
1.5. Cleaning and Maintenance:
Regular cleaning is crucial to prevent the accumulation of dirt, debris, or carbon deposits on the compressor wheel and expander impeller surfaces. Implement a maintenance schedule that includes cleaning procedures to uphold optimal performance over time.
2. Quality Assurance for Expander Impeller and Compressor Wheels at Arotec
The inspection for the impeller and compressor wheels in the recent Arotec company project was conducted in adherence to the inspection notification, following the Inspection and Test Plan (ITP). The tests conducted on the compressor wheel and expander impeller included an Overspeed test, Dimensional check, and Liquid Penetrant Test.
For the Overspeed test, there were four sub-steps:
2.1. Dimensional Check Before Overspeed Test:
Prior to the overspeed test, a dimensional check was performed on specified dimensions, as listed in the overspeed test report. The inspector verified the calibration certificates of measurement tools, ensuring they were within acceptable tolerances according to the working drawing. The initial dimensions were found to be within the acceptable range.
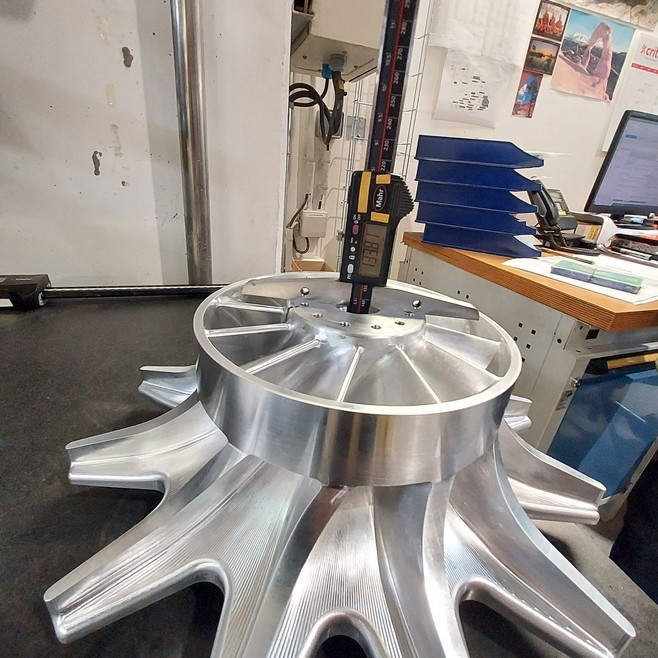

2.2. Overspeed Test:
The Overspeed test, conducted for 3 minutes at 21600 RPM, followed the test procedure. The calibration certificates of the testing machine were reviewed before the test, and the inspector witnessed the test. It’s important to note that the testing machine experienced fluctuations around the requested speed (±200 RPM) during the 3-minute duration.
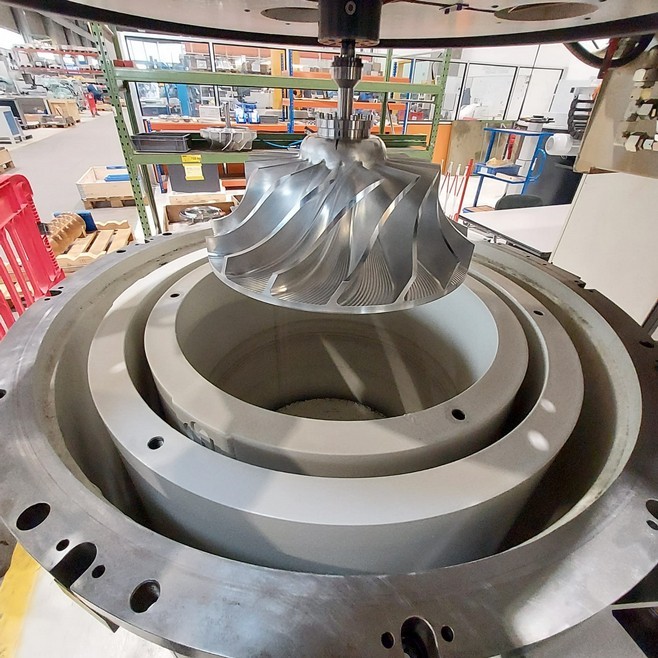

2.3. Dimensional Check After Overspeed Test:
Post the overspeed test, a dimensional check was performed on the specified dimensions. The controls showed that there were no changes in the initial dimensions, as expected.
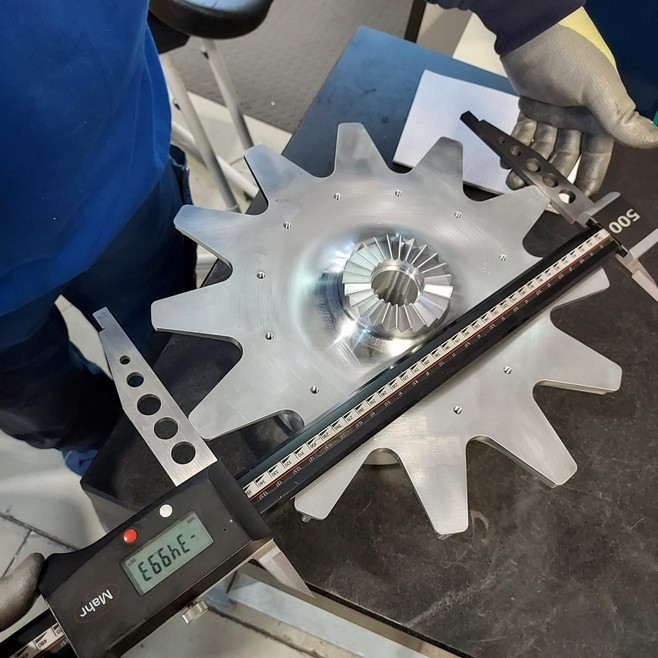

2.4. Liquid Penetrant Test (PT):
The PT test was conducted on the expander impeller. The penetrant was applied after the precleaning process, with a 20-minute dwell time. The excess penetrant was removed by water, and the drying time did not exceed 10 minutes. The final interpretation, conducted 10-20 minutes after the application of the developer material, revealed no defects. The related certificate of personnel involved in the PT was reviewed, and the test report is attached.
The mentioned tests, witnessed by an inspector, revealed no non-conformities, and the overall result was deemed satisfactory.
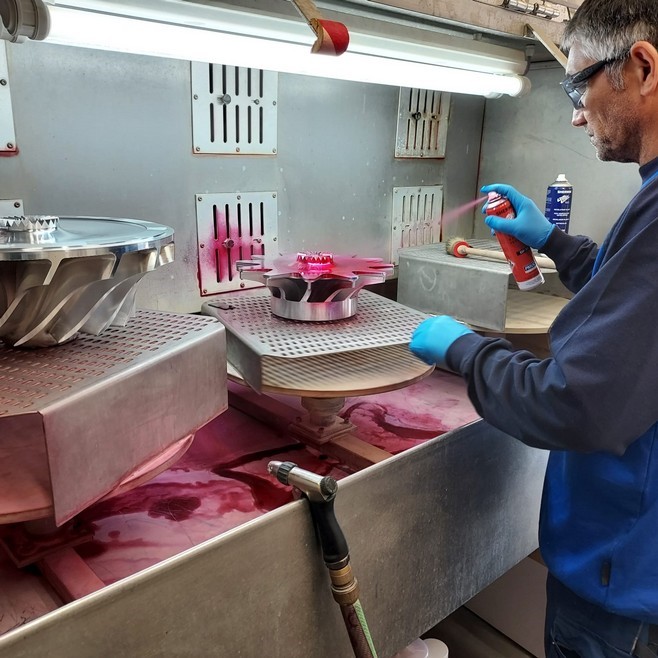

Similar procedures were followed for the compressor impellers in a separate set of tests, with the same inspection steps and outcomes. This included a dimensional check, an overspeed test, a dimensional check after the overspeed test, and a liquid penetrant test. The results of these tests were also satisfactory, and no non-conformities were found during the inspection process.
All in all, a thorough inspection of compressor wheels and expander impellers is essential for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of various systems that rely on these components. By focusing on material quality, blade condition, balancing, clearances, and overall cleanliness, operators can ensure that compressor wheels and expander impellers operate at peak performance levels. To ensure the peak performance of your systems, choose Arotec for unparalleled inspection services. Contact us today to schedule an inspection and elevate the efficiency of your components.