Electrical inspections of transformers play a pivotal role in ensuring the integrity of these vital assets to maintain the reliability of power systems and prevent costly downtime. Transformers are a fundamental component of the modern electrical infrastructure, serving as the silent workhorses that enable the efficient transmission and distribution of power.
The Transformers’ Role in Our Electrical World
Transformers are the unsung heroes of our electrical grid. They’re responsible for stepping up or stepping down voltage levels to facilitate power transmission over long distances or to deliver electricity to our homes and businesses at a safe and usable voltage. Without transformers, the modern world as we know it wouldn’t function.
However, transformers are not immortal; they age, degrade, and face operational challenges. Environmental factors, loading conditions, and manufacturing defects can all impact their performance over time. This is where electrical inspections come into play.
Electrical inspection of transformers
Electrical inspections of transformers are a systematic and comprehensive evaluation of these critical assets to ensure their continued safe and reliable operation. These inspections encompass a wide array of tests and measurements that assess various aspects of a transformer’s health and performance.

The Battery of the Transformer Tests
Electrical inspections involve an extensive battery of tests, each serving a unique purpose:
- Ratio and Polarity Tests: These tests confirm that a transformer is operating within its specified voltage ratios and phase angles.
- Winding Resistance Measurement: By measuring winding resistance, inspectors can identify issues like loose connections, corrosion, or deterioration.
- Insulation Resistance Test: This test ensures that the insulation between windings and ground remains acceptable, preventing electrical leakage.
- Turns Ratio Test: This test verifies that the transformer’s turns ratio meets design specifications.
- Partial Discharge Measurement: Detecting partial discharges helps identify issues within the insulation system that could lead to future failures.
- Dielectric Dissipation Factor Test: This test examines the dielectric properties of insulating materials and helps identify issues with dielectric loss.
- Transformer Turns Ratio Test: Inspectors use this test to determine the transformer’s turn ratio, helping identify problems with the windings.
- Short Circuit Impedance Test: This test assesses the transformer’s impedance and helps evaluate its capability to withstand short-circuit conditions.
- Sound Level Measurement: It gauges the sound produced during transformer operation, ensuring it stays within acceptable limits.
- Visual Inspection: A visual examination assesses the transformer’s physical condition, looking for signs of overheating, corrosion, or other issues.
The Importance of Regular Inspections
Regular electrical inspections are vital for several reasons:
1. Safety: They ensure that transformers are operating safely and do not pose hazards to personnel or property.
2. Reliability: Inspectors prevent costly breakdowns and outages by identifying potential issues early.
3. Efficiency: Well-maintained transformers operate more efficiently, reducing energy losses.
4. Compliance: Many regulatory authorities and standards require regular transformer inspections.
5. Environmental Impact: Efficient transformers contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions.

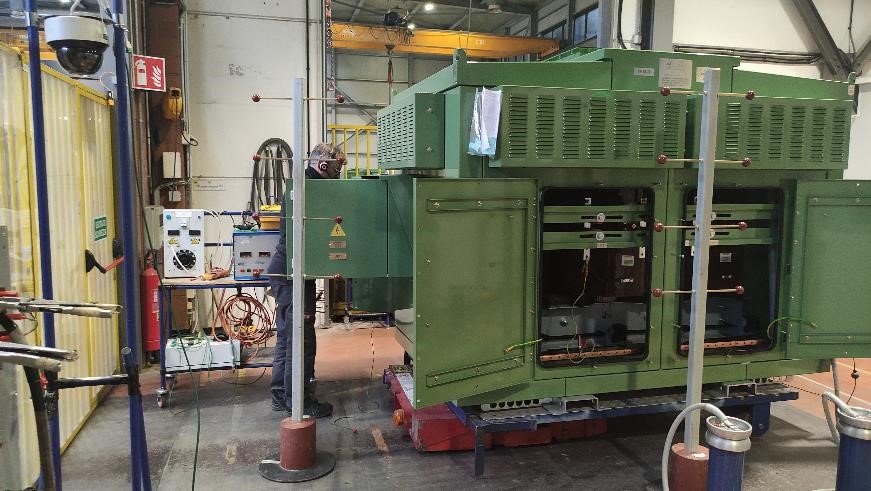
Recently, Arotec, a leading name in the field of electrical inspection, has undertaken a groundbreaking commission in the realm of transformer inspection.
The project not only underscores the significance of regular transformer inspections but also showcases Arotec’s unwavering commitment to electrical safety and reliability.
Let’s delve into this remarkable endeavor, exploring the intricacies of transformer inspection, and its implications for the broader field of electrical engineering.
The inspection conducted at Hitachi Switzerland on October 19th and 20th, 2023, was a comprehensive and rigorous assessment of the four Transformers, with the primary goal of performing Factory Acceptance Tests (FAT). These tests encompassed a diverse range of electrical evaluations, each designed to scrutinize the Transformers’ performance and integrity under various conditions.
The battery of assessments commenced with the “Measurement of Voltage Ratio and Phase Displacement,” a meticulous examination that scrutinized the primary and secondary voltage ratios in no-load conditions. Additionally, it precisely determined the turn ratio, setting stringent tolerances to define the threshold of acceptability.
The “Resistance Test with Applied Voltage” delved into the high-voltage (HV) system’s intricate interplay with low-voltage (LV) circuits, probing the HV creepage and clearance distances. It imposed a demanding challenge by applying voltage, demanding that the transformer successfully endure it for a specified duration.
The “Induced Overvoltage Withstand Test” raised the stakes by subjecting the transformer to voltages double the working voltage, spanning adjacent turns, layers, and phases. This test was pivotal in affirming the insulation’s robustness and its ability to withstand the heightened voltage, all while maintaining minimal test current.
“No-Load Losses and No-Load Current” measurements were conducted to unveil the transformer’s characteristics at rated voltage and frequency. This test observed stringent tolerances on component losses, ensuring they met predefined criteria.
The “Measurement of Winding Resistance” exercise utilized direct current measurements, carefully matching these values with the calculated ones, thereby attesting to the transformer’s adherence to precise specifications.
“Measurement of Short Circuit Impedance and Load Losses” sought to elucidate the transformer’s performance under load conditions, closely inspecting impedance voltage at rated current and frequency.
The “Basic Lightning Impulse (BIL) Tests” introduced a real-world perspective, simulating over-voltage conditions reminiscent of atmospheric discharges. This assessment included both standard and chopped lightning impulses, pushing the transformer’s insulation to the limits.
The “Partial Discharge Measurement” examined the transformer’s behavior when subjected to partial discharges, enforcing specific criteria for acceptable results.
To gauge its real-world performance, the “Temperature Rise Test” assessed the temperature rise of the transformer windings under no-load and short-circuit conditions, critically scrutinizing its adherence to prescribed nominal values.
The “Insulation Resistance Test” aimed to evaluate the transformer’s insulation quality and confirm the negligible leakage current, emphasizing the importance of a high insulation resistance measurement.
“Measurement of Capacitance and Dissipation Factor (Tan Δ)” delved into the transformer’s power factors, imposing strict criteria for acceptability.
“Measurement of Sound Pressure Level” ventured into assessing the transformer’s acoustic output during operation, aligning with predefined standards.
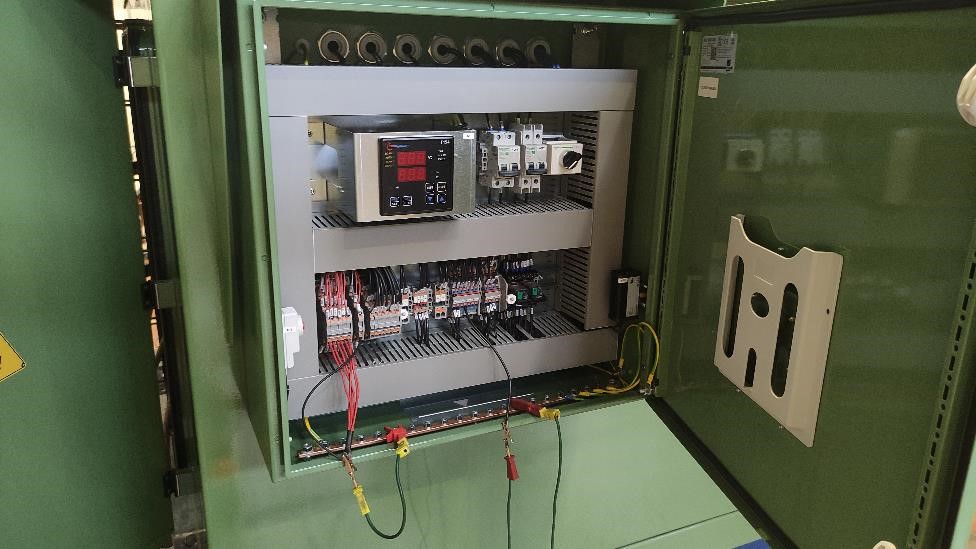
The “Insulation of Auxiliary Wiring” test verified the safety and compliance of the auxiliary power and control circuitry, ensuring insulation met established standards.
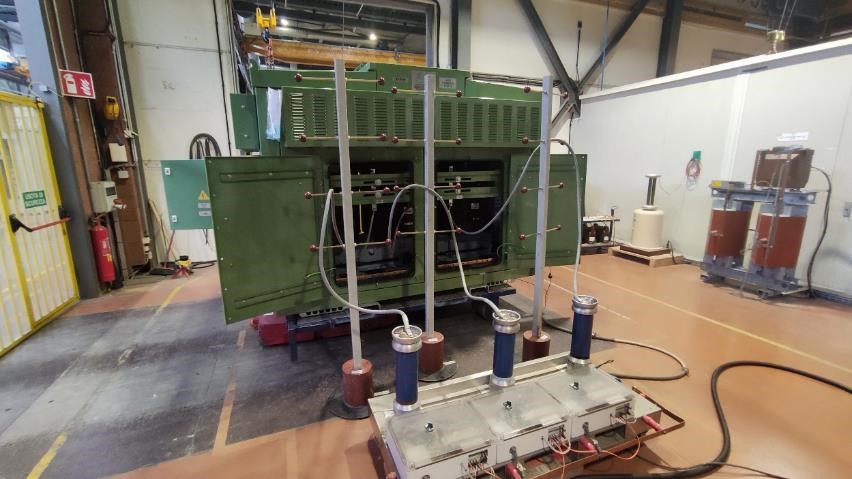

Finally, the “Visual Inspection and Check of Auxiliary Devices” exercised meticulous visual scrutiny, ensuring the equipment’s cleanliness, integrity, and functionality aligned with the highest standards.
Moreover, each transformer underwent an exhaustive “Check of the Rating Plate,” ensuring the accuracy and indelibility of the displayed information.
Collectively, these assessments have produced satisfactory results and meticulous documentation, reflecting the unwavering commitment to the quality and integrity of the Transformers under scrutiny.