Abstract
This article is mainly about “Paint Testing” which is to be applied to industrial products including the common methods under the presence of the third party inspection. You can read “paint inspection – part1” here
Paint Testing-Introduction
In the previous article, some general requirements, which are applied to the paint to ensure the quality of that were described. In the current article, some extra common tests are mentioned. Due to the service, which the equipment is applied, the corrosive substances to be in touch with the equipment, working temperature, and other parameters, some tests could be performed. The test procedure specifies these tests and the customer will be notified of these tests. Moreover, the client could ask for some extra tests, to achieve further information. The third-party inspection agency “TPIA” as an independent side, provides the inspection services in this regard. The inspection will be carried out based on the approved reference documents by witnessing the “Paint Testing”, and the inspection report along with the test reports describes the quality of paint including the measured mandatory parameters.
1- What’s the purpose of the “Adhesion Test”
This test is applied to the dried coating to be ensured, whether the paint has adhered properly to the base substrate or not. There are some types of adhesion test, which based on the relevant standard and technical specification, specifies in the test procedure that which test method should be applied.
1-1- CrossCut Method A: “X-Cut”
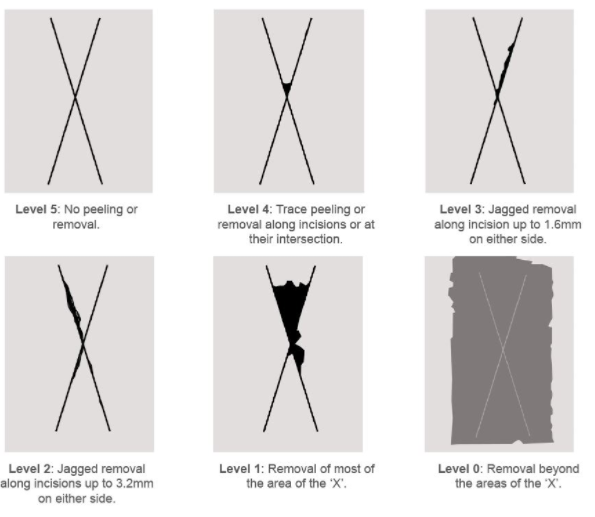
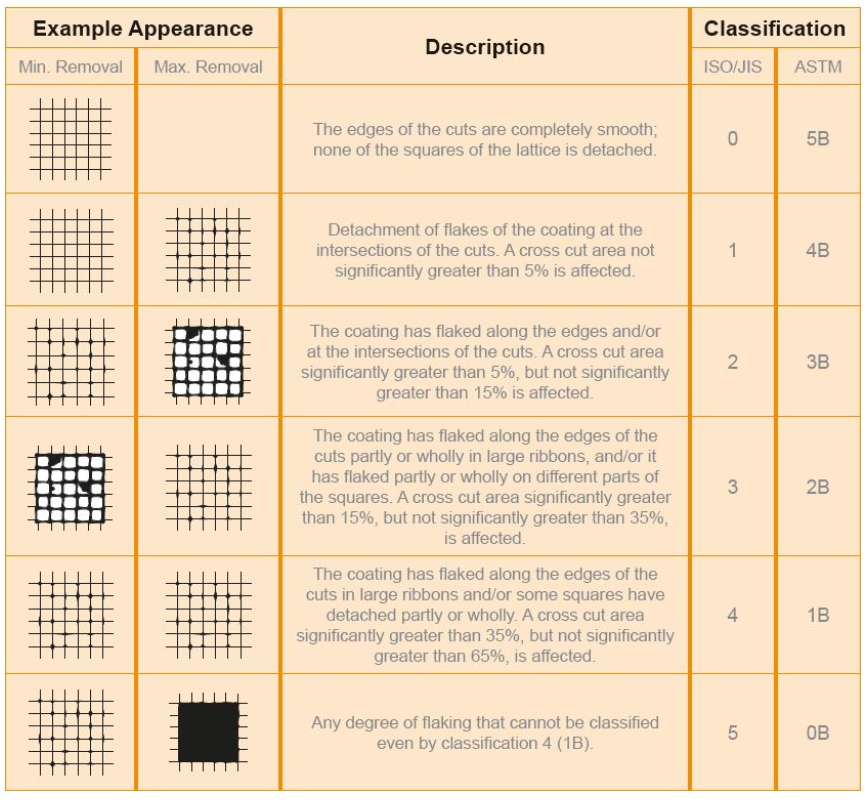
This test is performed usually on the coating thickness of over 125 µm (5mils). This test is applied generally on the steel, however, it can be done also on softer material such as wood or plaster. An “X” should be made on the coating through a cutting device e.g. razor blade, knife, etc., with a specific length and angle, the depth of cut should be deep so that the base material could be visible, otherwise another “X-cut” should be made. The scratched surface is cleaned by a brush and in the next step, a piece of specific tape will adhere to the X cut and after the tape was pulled off and applied on the surface properly, the tape is removed by hand. Finally, the observation should be evaluated against the specified standard in the test procedure. ASTM D3359 as an important common standard could be mentioned.
1-2- Cross-Cut-Method B: “Cross Hatch Method”
This test is performed usually on the coating thickness under 125 µm (5mils). This test is applied generally on the steel, however, it can be done also on softer material such as wood or plaster. A cross-hatch should be made on the coating through a cross-hatch cutter, with a specific length with a 90° angle, moreover, the number of blades was specified in the reference standard. The depth of cut should be deep so that the base material could be visible, otherwise, another cross hatch should be made. The scratched surface is cleaned by a brush and in the next step, a piece of specific tape will adhere to the prepared surface and after the tape was pulled off and applied on the surface properly, the tape is removed by hand. Finally, the observation should be evaluated against the specified standard in the test procedure. ASTM D3359 as an important common standard could be mentioned.
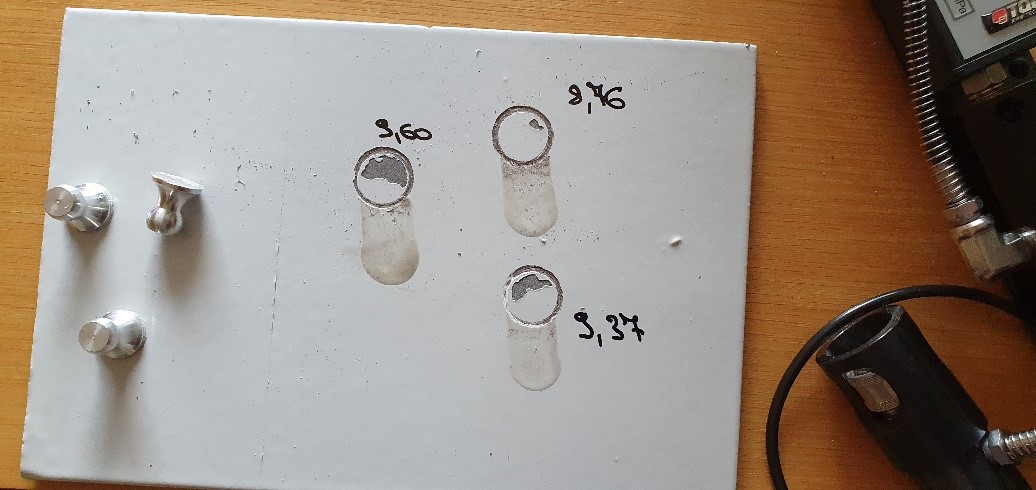
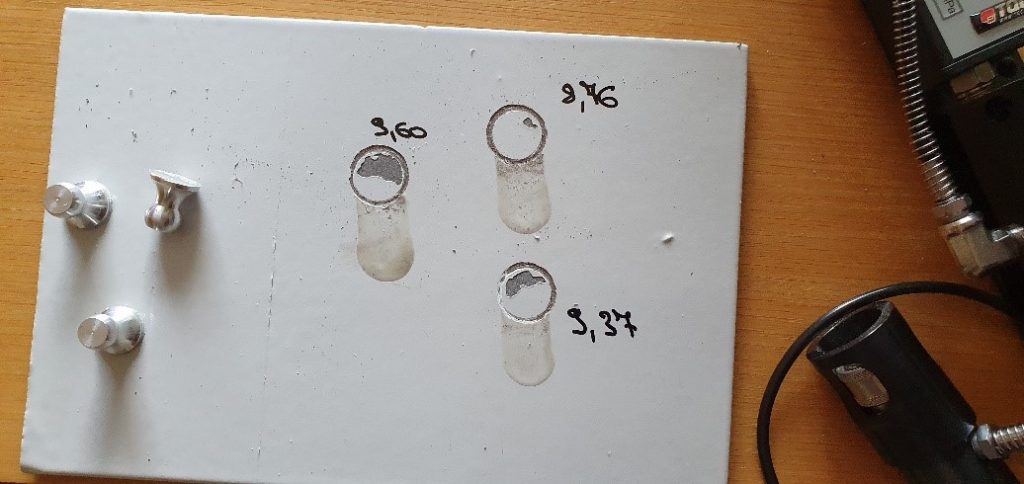
1-3- Paint Testing- Pull-off test
The pull-off test is carried out by some loading fixture called “dolly”, which should be adhered to the dried and cleaned painted surface. The moisture and temperature should be measured and compared with the standard because those can affect the test results. Then a pull-off adhesion tester is applied to apply the tensile force on the dolly. By increasing the force the tensile strength is monitored and measured till a part of the paint, which is adhered to the dolly to be pulled off. By this method, the maximum tensile strength of the coating could be measured and compared with the acceptance limit. ASTM D 4541 and BS EN ISO 4624 are two common standards of the pull-off test.

The third-party inspection representative witnesses the “Paint testing” and report the observation to the client along with the test reports including the compliance or any non-conformities to specify the needful action to be done to achieve the acceptable results.