Abstract
This article discusses the “Pipe- during production inspection” and the activities, which are performed by third-party inspection as an independent inspection agency to check the quality and quantity of products during the pipe production.
Introduction:
“Pipe- during production inspection” including various steps were described in the first and second parts.
In the third part, it was tried to describe the steps related to the finishing and final inspection.

1- Why the Hydrostatic pressure test should be applied?
The Hydrostatic pressure test is carried out on the pipe to check the strength of the produced pipe in comparison with the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP). The testing parameters such as water temperature, test pressure, chloride content, and so on are controlled during the test by third-party inspection. Any deformation or pressure drop should be compared with the related acceptance criteria, whether the tested item could be accepted or must be rejected.

2- Threading inspection for threading pipes
2.1
For the threaded pipes, the threading dimensions should be controlled based on the related standards on length, thread length, depth, and angle, and so on in accordance with the specified tolerances. The technical inspector witnesses the threading control based on the specified intervention in the inspection and test plan for TPI.

2.2- Which instruments are used for threading inspection?
The inspection instruments which are used during the threading inspection are generally divided into dimension measuring tools (e.g., caliper, micrometer, borescope,…) and thread gauges (e.g. go-not go gauges)

2.3
After the successful threading inspection, the thread protection cap is used to achieve the proper preservation.

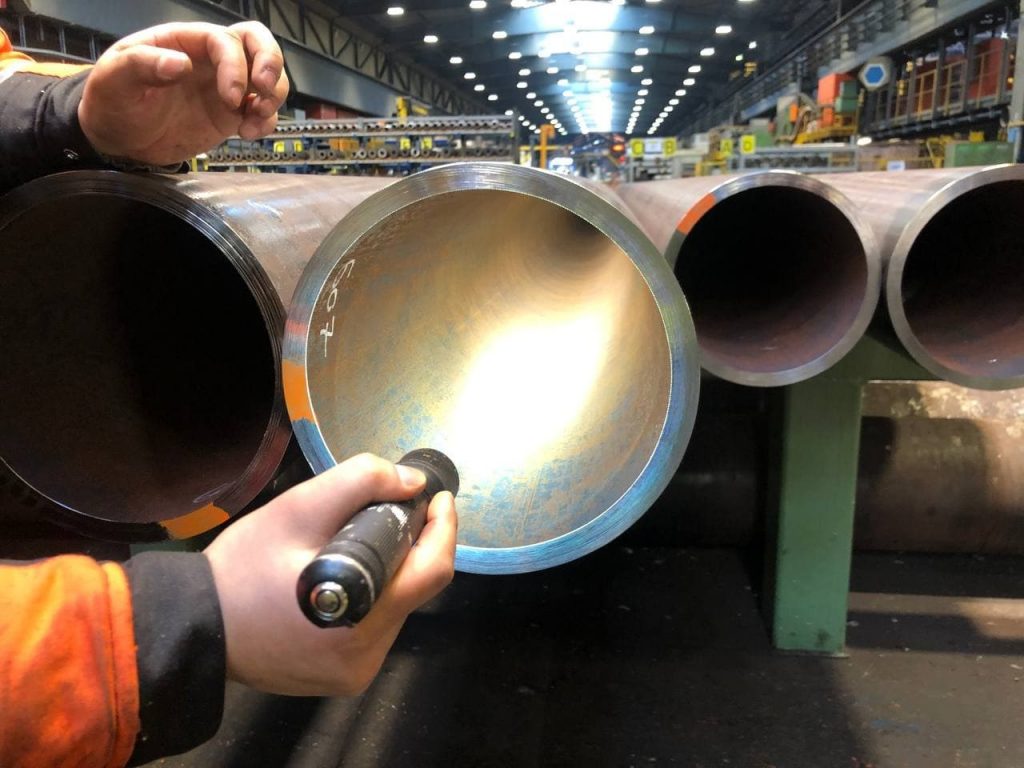
3- Visual inspection on “Pipe-during production inspection”
As a final part of “pipe-during production inspection,” a visual inspection should be performed internally and externally at the end of the fabrication process to ensure the pipes are in the proper status without any surface flaws, painting, and welding imperfection, or any unacceptable deviations.

The TPI representative reports any deviations or discrepancies to the customer for further needful action.

4. Pipe inspection-Drift test:
The purpose of performing the drift test is for the ovality and inner diameter of the pipes to be controlled. The test is performed by a cylindrical gauge through the length of the pipe. Therefore any unaccepted inner diameter or deviation in roundness could be monitored and observed. The third-party inspector witnesses the test and controls the results. Finally, the results will be reported to the client.

5. Dimensional check:
The dimensions such as outside diameter, wall thickness, and length values are checked according to the reference documents by the calibrated instruments and tools with the attendance of the inspector.

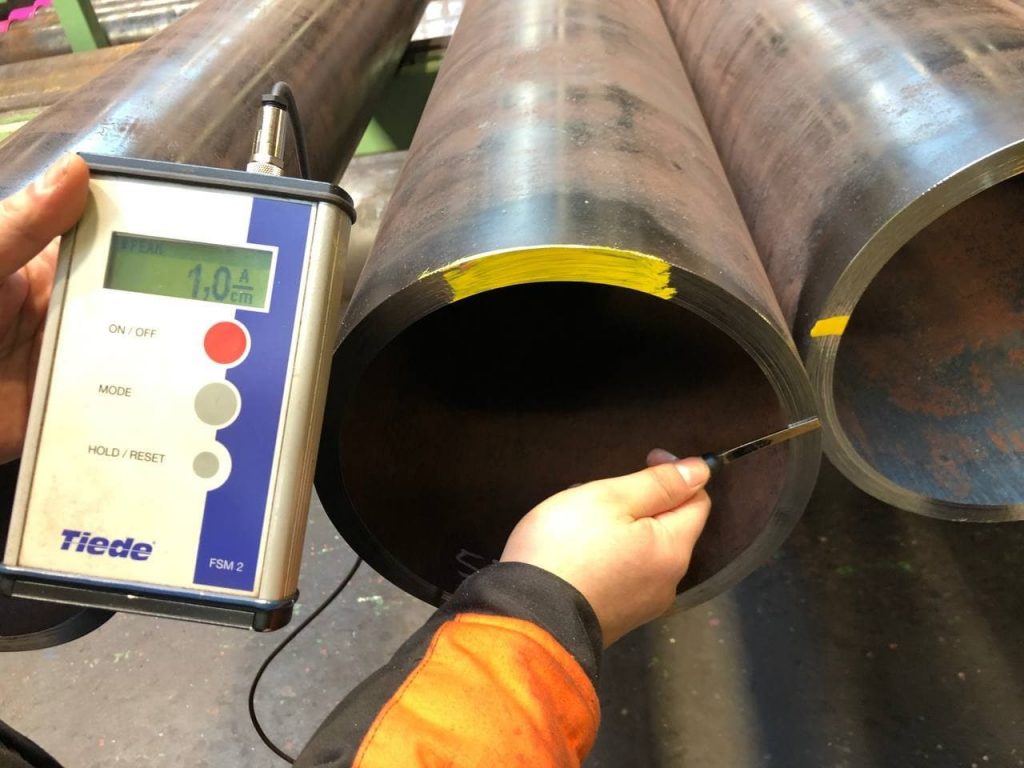
6. Residual magnetism control
As a step of pipe inspection, the residual magnetism, which probably remains from the manufacturing process on the steel pipes should be controlled and to be within the range of the acceptance limit.

7- FINISHING – MARKING
A mill coating is applied on an external surface of the products. Then the marking is printed or engraved on pipes according to the related procedure and reference documents.

Moreover, the grade marking and color codes are checked according to the reference specification.

Conclusion:
It should be mentioned, due to various types, materials, and pipe usages, there are so many tests, which could be surveyed by the third-party inspection agency to be ensured if the ordered products comply with the international standards or specific technical requirements of the customer. During the production, an inspection provides not only the final quality control but also the parameters, which should be controlled in the manufacturing process to reach the all of requirements.